Mettez en œuvre Zero Trust pour éviter les coûts exorbitants liés aux temps d'arrêt
The financial impact of a cyberattack is not limited to only the cost of remediating the network and its hardware; it also includes potential ransom payments, possible brand damage, and lost revenue due to downtime. In response to an increasing number of breaches, business leaders across industries are finally taking the downtime caused by attacks more seriously, knowing that their data, their reputation, and their bottom line are all at stake.
In this post, I'll explore that further, along with strategies to reduce the impact of breaches and your risk of downtime.
From minutes to millions
The average downtime as a result of a ransomware attack is around 16 days, reports show that the cost of one minute of downtime could reach tens of thousands of dollars, with a single day of downtime‚ costing as much as 13 million dollars. These statistics demonstrate how limiting downtime during ransomware attacks could save millions of dollars. This, in turn, makes clear the necessity of investing in security measures that reduce, if not prevent, downtime following a cyberattack.
According to the National Security Agency, using a Zero Trust model to secure a data centre, public cloud, and endpoints largely prevents propagation of a ransomware attack, which subsequently reduces downtime for the business.
Forrester Research concluded that Zero Trust can mitigate an organization's risk exposure by 37% or more and reduce security costs by 31%, which helps save millions of dollars in overall IT security budgets.
Reducing downtime with Zero Trust Segmentation
During a cyberattack, many businesses look to protect IT systems from infection by pre-emptively removing their connectivity. This often involves shutting down yet-to-be-infected systems or restricting an employee's ability to perform their revenue-generating activities. This is critically disruptive to the business, as exemplified by the unmitigated spread of malware across a major global aluminum producer that resulted in the shutdown of manufacturing, costing an estimated 80 million dollars.
This is where microsegmentation, an essential component of Zero Trust security, comes in: it makes shutting down yet-to-be-infected systems unnecessary because it prevents the lateral movement of attackers.
Host-based micro-segmentation makes it easy to move infected systems into quarantine, whether with an API call or with a single click that automatic recalculates the rules for the connected systems.
Additionally, it allows unaffected systems to talk only to other unaffected systems. It does not require changing the network, "pulling the plug," or redefining zonal firewall rules.
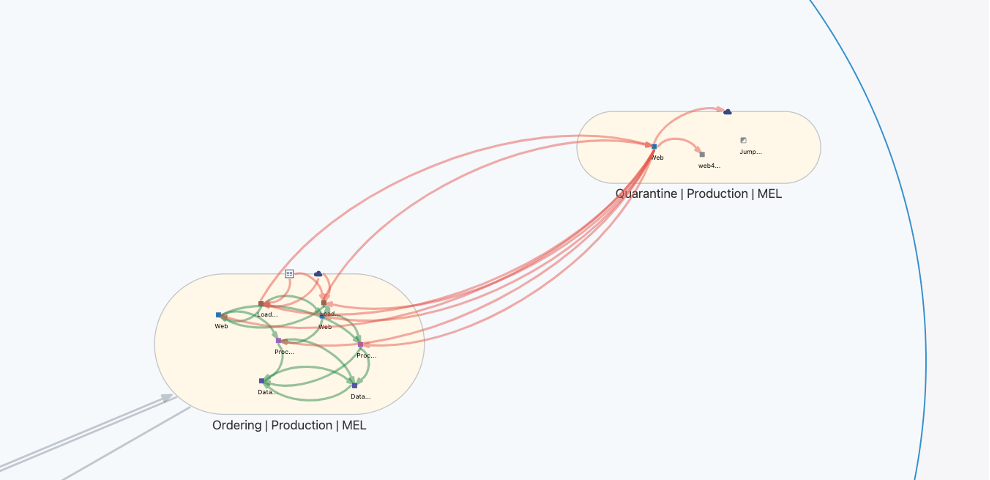
A quarantine policy also restricts all inbound and outbound connections from an infected system, while still allowing SSH/RDP access from a management network. This method has two important benefits:
- It allows business services not yet reached by the attack to continue, preventing unnecessary downtime and business disruption.
- It preserves the in-memory state of the infected system and logs, which can then be utilized by forensics teams to further understand the attack.
Gaining Zero Trust control during an attack
What if you are under attack but have not implemented Zero Trust? It might not be too late to avoid catastrophic downtime. The speed with which you can deploy host-based micro-segmentation is critical, and with some degree of automation and orchestration, this can be achieved even in the middle of an attack. IT can define the quarantine micro-segmentation policies from above and then move identified infected workloads into quarantine while the attack is ongoing. Adopting a protocol like this would help in two concrete ways: First, it provides visibility of application connectivity, which would enable an educated incident response. Second, it helps IT gain control of the infected systems fast enough to prevent the lateral spread of the threat.
Nevertheless, adopting Zero Trust and preventing lateral threat movement through micro-segmentation should be the long-term strategy for all organizations. Being a few steps ahead of the threat is always a better security posture than working to limit the blast radius after a breach has occurred.
A first-of-its-kind report by Bishop Fox, a security consulting company, quantifies the efficacy of micro-segmentation. The report outlines a testing methodology that can help organizations validate results in their own environments. Through implementation of the MITRE ATT&CK framework, Bishop Fox conducted several rounds of testing against varying degrees of policy granularity to measure the ability of micro-segmentation to effectively limit lateral movement.
Zero Trust requires a mindset shift among leadership
Working towards Zero Trust requires IT leadership to embrace a new mindset, new principles, and new technologies. With the widespread shift to remote work, the need for Zero Trust in data centers and clouds and on endpoints has only increased. The effort that organizations put into Zero Trust security is well worth it to avoid potentially crippling costs of downtime from the inevitable breach.
Learn how organizations like Cathay Pacific and HGC are using host-based micro-segmentation from Illumio to reduce this risk and accelerate their Zero Trust journeys.
.png)


.webp)